|
|
MECHANICS ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION ANIMATION
Ian Cooper School of Physics, University of Sydney ian.cooper@sydney.edu.au
DOWNLOAD DIRECTORY FOR MATLAB SCRIPTS
em_emf_1.m Matlab used as a drawing package to produce an animation of the emf induced as a magnet passes through a coil.
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION SIMULATION
· A changing magnetic flux induces a changing electric field · The changing electric field induces an emf in a conductor. · In a conductor loop, the changing emf induces a current.
The above processes are known as electromagnetic induction. This result is known as Faraday’s law.
Carefully watch the animation many times of the magnet passing through a solenoid (coil). Memorize the sequence of events so that you have a better understanding of the electromagnetic induction process.
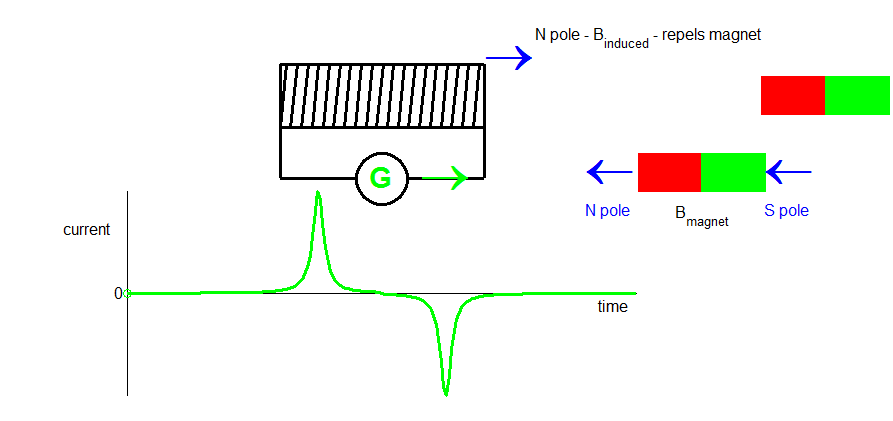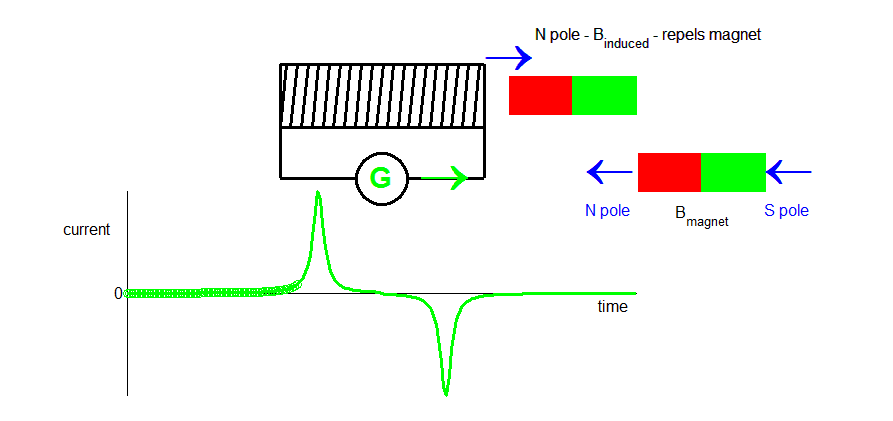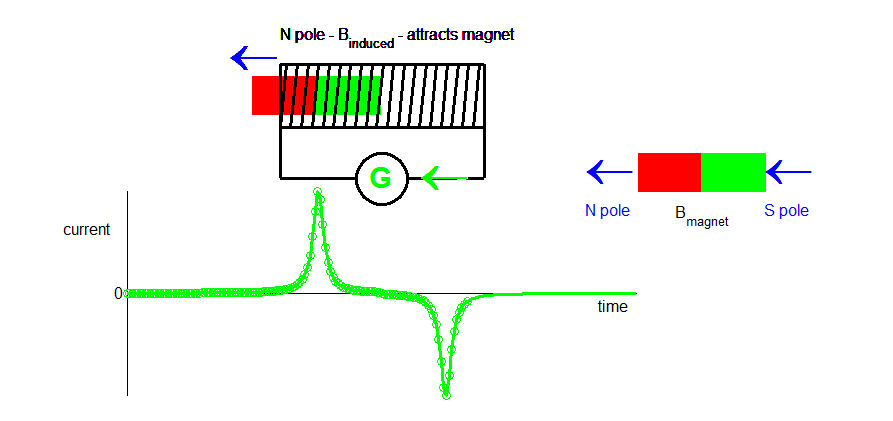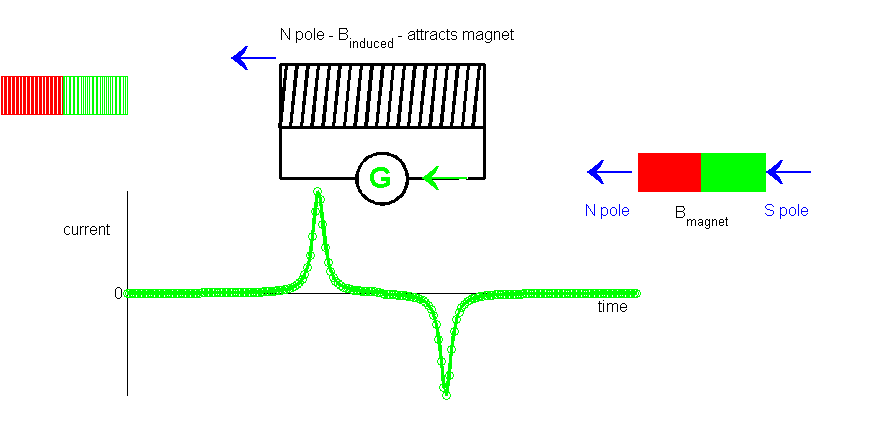
As the north pole of the permanent magnet approaches the coil, an induced current is setup within the conductive loops.
Lenz’s law – the induced emf and induced current are in such a direction as to oppose the change that produces them.
Therefore, the direction of the current is such that the induced magnetic field opposes the motion of the motion of the permanent magnetic towards the coil – the left of the coil corresponds to a South pole and the right side a North pole (North pole repels a North pole).
When the permanent magnet is at the centre of the solenoid the change in magnetic flux is zero and the induced current falls to zero.
As the permanent magnet exits the solenoid, the changing magnetic flux induces a current in the opposite sense to when the magnet entered the solenoid. The North pole is now on the left and the South pole on the right. The induced North pole on the left attracts the South pole of the magnet to oppose the motion of the magnet away from the solenoid.
|
|