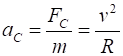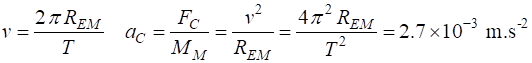|
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE 5
ADVANCED MECHANICS P50 005.m (A) What is
Newton’s inverse square law of gravitation? What is the
meaning of the terms: centripetal force and centripetal acceleration? (B) Newton tested
his inverse square law of gravitation by comparing it to the gravitational
and centripetal acceleration of the Moon in its orbit about the Earth. What
did Newton conclude about his answers?
To help answer this question, calculate the gravitational acceleration
of the Moon to the Earth and calculate the centripetal acceleration of the
Moon. Earth-Moon distance Period of Moon orbiting
Earth T = 27.3 days Mass of Earth ME = 5.97x1024 kg Universal gravitational
constant G = 6.67408x10-11 N.m2.kg-2 View solution below only after you have completed the answering the question. |