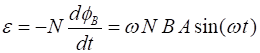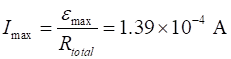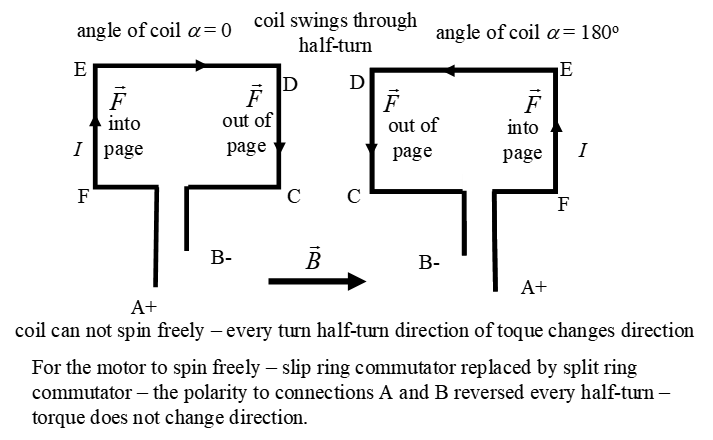|
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE
6 ELECTROMAGNETISM
P60 017
Consider the generator
shown in the diagram with the parameters
magnetic field B
= 1.25 T
LCD = LEF = 12 mm
LDE = LCF = 6.0 mm
Rotation rate 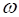 = 20 rpm (revolutions per minute) = 20 rpm (revolutions per minute)
Number of turns of coil N = 100
Total resistance of coil Rcoil = 10 W
Resistance of external load connected between A and B Rload
= 125 W

(A)
Calculate:
Angular frequency w =
? rad.s-1
Frequency of rotation
f = ?
Hz
Period of rotation T
= ? s
Maximum magnetic flux fB = ? T.m2
Maximum induced emf (polarity of point A
w.r.t to the point B)
emf
= ? V
Maximum induced current in the circuit I
= ? A
(B)
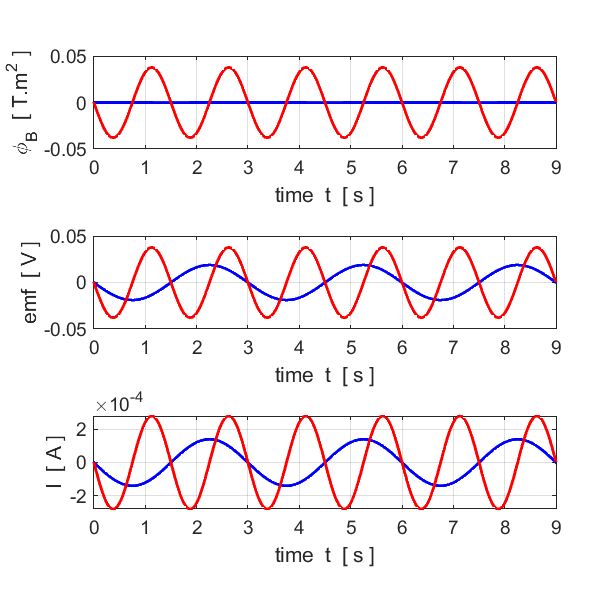
Sketch the time graphs for the quantities: magnetic flux; induced emf; induced current.
(C)
On your graphs add curves to show the resulting changes that would
occur if the rotation speed was doubled.
The generator is now to be used a
motor. The coil is no longer rotated by an external mechanical energy supply
and the load is removed from between A and B.
The point A was connected to the
positive terminal of a 12 V battery and point B was connected to the negative
terminal.
(D) Explain why this arrangement
does not work as a motor.
(E)
The commutator of the slip rings is replaced by a split ring. The
motor now works. Why?
View solution below only after you have completed the
answering the question.
|