|
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE 7.1 THE NATURE OF LIGHT
QUANTUM MODEL P71 009 (A) Scientists tried to explain
observations of blackbody radiation using classical wave theory and then
quantum theory. (A1) What is meant by the term blackbody radiation. (A2)
What was a limitation of
classical wave theory that could not explain blackbody radiation? (A3) How does quantum theory satisfactorily explain
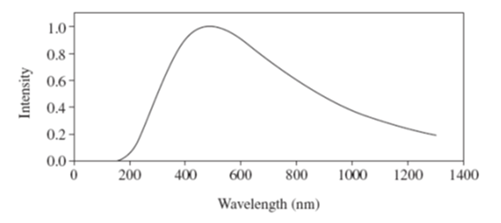
blackbody radiation? (B) The graph shows the intensity–wavelength relationship of electromagnetic radiation emitted from a blackbody cavity. In 1900, Planck proposed a mathematical formula that predicted an intensity–wavelength relationship consistent with the experimental data. The success of this formula depended on what hypothesis? Comment on the curve shown.
View solution below only after you have completed the answering the question. |
|
Solution (A) (A1) Blackbody - object which gives the maximum amount of energy radiated from its surface at any temperature and wavelength and the absorbs all the radiation that falls on it. (A2) JWS Rayleigh
& James Jeans Math model described blackbody radiation curves at long wavelengths accurately but not at shorter wavelengths in the UV, radiation from cavity absorbed and re-emitted with ever smaller and smaller l, energy emitted from cavity becoming infinite – UV catastrophe (A3) Max Planck was the first person to give a qualitative explanation of the curves for the radiation emitted by a blackbody. He assumed that energy is quantized. The change in energy of an oscillator is a nhf where n is an integer (B) Max Planck (19 Oct 1900) - hypothesis – radiation emitted & absorbed by walls of a blackbody cavity – radiation quantized Change in energy | E2 – E1 | =
n h f n
= 1, 2 3, … His assumption of energy levels quantized enable him to obtain an equation to successfully describe the blackbody radiation curve: Planck radiation law – agreed with experiment. Each atom behaved as a small antenna (electromagnet oscillator) – energy of an oscillator n h f (n = 0, 1, 2, ….) - energy of oscillator was quantized. Change in energy of oscillator (emission & absorption) quantized DE = integer ´
h f Þ atomic oscillators do not radiate or absorb energy in continuously variable amounts Birth of Quantum Physics - Planck did not believe that atomic oscillators behaved this way - used his model to simply account for the shape of the blackbody curve Curve shows the radiation emitted from a blackbody at a fixed temperature. The temperature determines the peak in the curve Wien’s Displacement Law lpeak T = constant The total area under the curve represents the rate of the total energy emitted by the blackbody. |