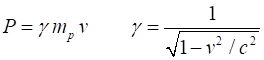|
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE 8.2 FROM THE UNIVERSE TO THE ATOM
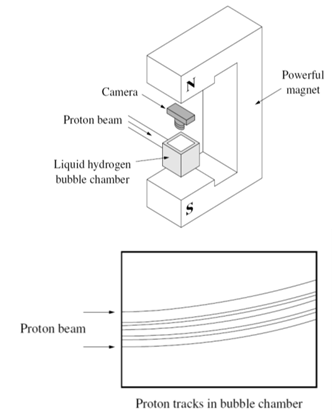
THE NUCLEUS P82 003 Bubble
chambers are used in conjunction with particle accelerators to
photographically record the tracks of fast-moving charged particles. An
intense magnetic field is applied at right angles to the path of the
particles to deflect them according to their charge and momentum. The diagram
shows a beam of protons travelling horizontally at 8.00´107 m.s-1 and entering a liquid
hydrogen bubble chamber in a vertical magnetic field of 1.82 T. Examination
of the photograph taken by the camera, as sketched below, shows that the
protons were deflected along a circular path of radius 0.480 m. qp
= 1.602x10-19
C
mp
= 1.6726x10-27
kg
c = 3.00x108 m.s-1
(A)
Comment on the mass of the accelerated proton. (B) Derive an
expression for the momentum of a proton from the forces it experiences in
this experiment. (C) Calculate
the momentum of a proton in the bubble chamber. (D) Compare the answer in (C) with the
relativistic momentum of a proton. View solution below only after you have completed the answering the question. |
|
Solution qp
= 1.602x10-19
C
mp
= 1.6726x10-27
kg
c = 3.00x108 m.s-1 v = 8.00x107 m.s-1 B = 1.82 T R = 0.35 m q = 90o (A) The
modern view in special relativity is that the mass of the proton is a
constant and independent of its velocity. It is the momentum of the proton
that is now considered to be a function of its velocity. momentum of
proton (B) Magnetic
force = centripetal force
(C) Momentum of proton from experiment
(D) Relativistic momentum
There is a good agreement between the two values of the momentum of the proton. |