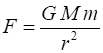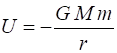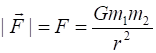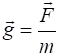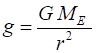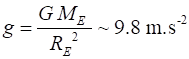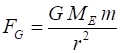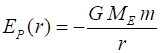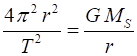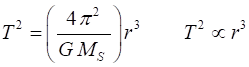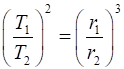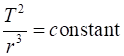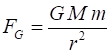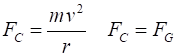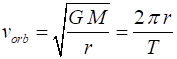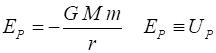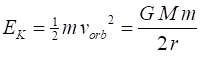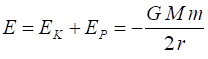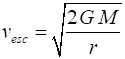MODULE 5
ADVANCED MECHANICS
SUMMARY: MOTION IN
GRAVITATIONAL FIELDS
|
SYLLABUS EQUATIONS Gravitational force (magnitude) Gravitational potential energy Keplers Third Law GRAVITATIONAL FIELD
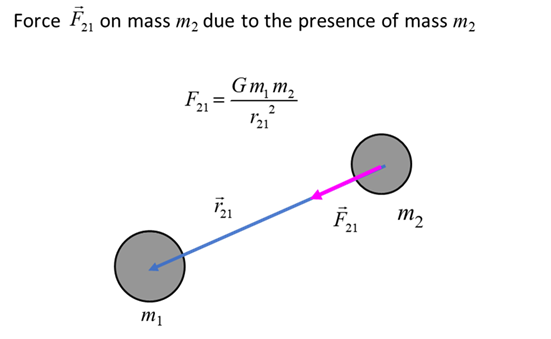
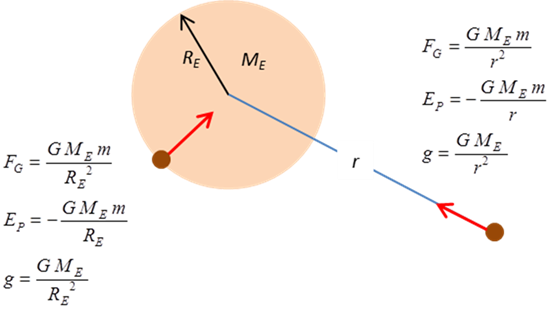
Newtons Law of Universal
Gravitation (attraction between two masses)
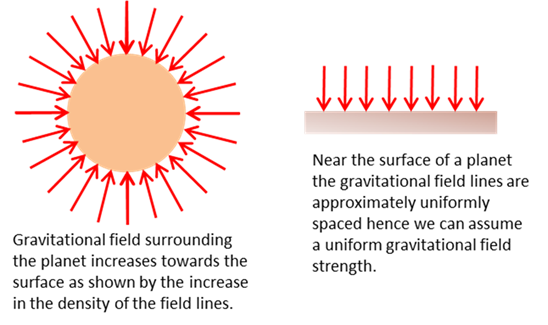
Gravitational field strength Gravitation field strength
surrounding the Earth Gravitation field strength at the
Earths surface
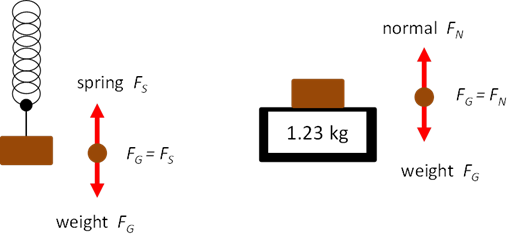
Weight
Work Gravitational force of the Earth Gravitational field strength
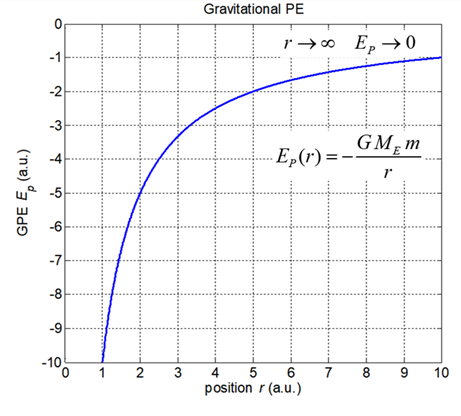
(acceleration due to gravity) Gravitational potential energy near
the Earths surface The Earths gravitational potential
energy
Conservation of
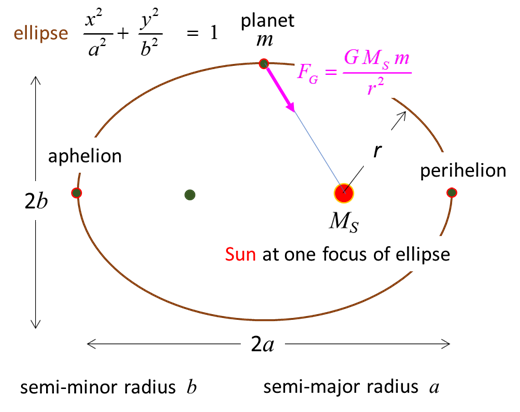
energy MOTION OF PLANETS Keplers First Law: A planet describes an ellipse
with the Sun at one focus.
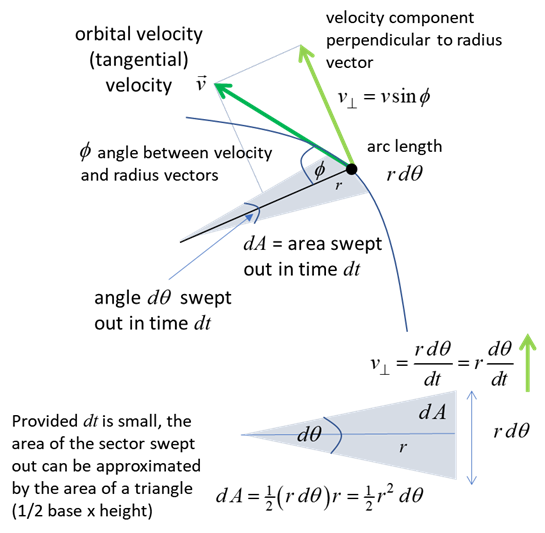
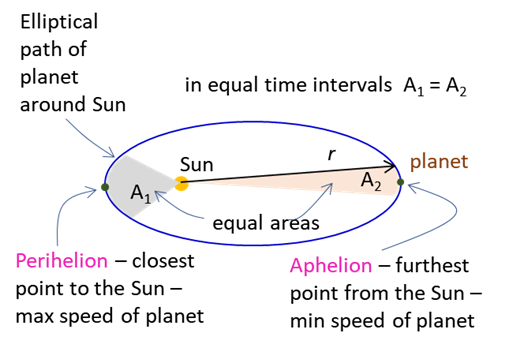
Kepler's Second Law: Each planet moves so that an
imaginary line drawn from the Sun to the planet sweeps out equal areas in
equal periods of time.
Keplers Third Law:
MOTION OF
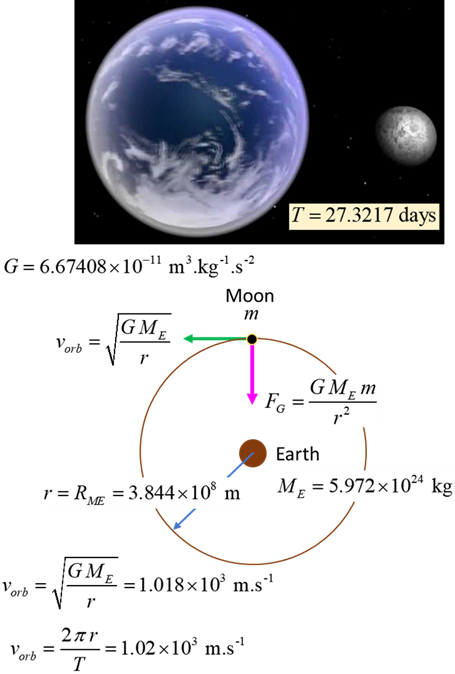
SATELLITES Orbital motion of object of
mass m about a massive object of mass M (m << M assume M stationary w.r.t m) with an orbital radius r, orbital speed Gravitational force (magnitude) Centripetal force (magnitude) Orbital speed (circular orbit) Angular momentum Gravitational potential energy Kinetic energy (circular orbit) Total energy (circular orbit) Conservation
of energy Escape speed |
|
Ian Cooper School of Physics University of Sydney If you have any feedback, comments,
suggestions or corrections please email Ian Cooper ian.cooper@sydney.edu.au |