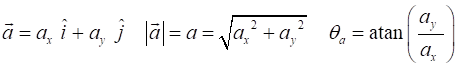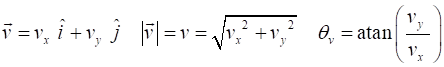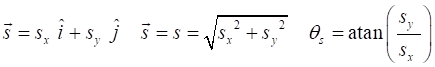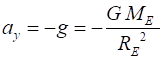MODULE 5
ADVANCED MECHANICS
SUMMARY: [2D] MOTION
(PROJECTILES)
|
SYLLABUS EQUATIONS
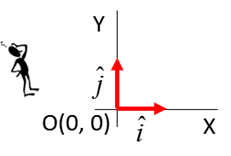
FRAME OF REFERENCE
Origin O(0,0, 0) reference
point Cartesian
coordinate axes (X, Y, Z) Unit
vectors Specify
the units [2D] Motion with
constant acceleration When the object is moving with a uniform (constant) acceleration, the equations
describing the motion for the time interval t between Event #1
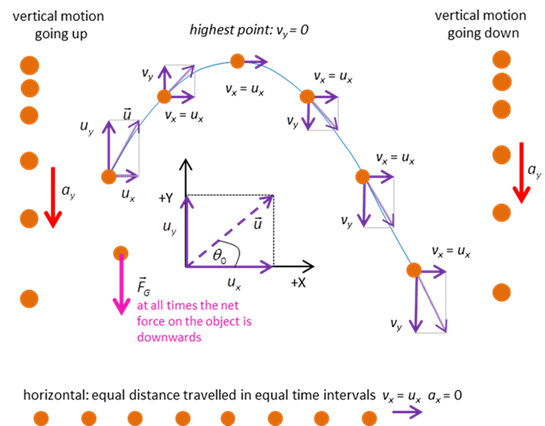
(initial values) and Event #2 (final values) are time acceleration velocity displacement vectors PROJECTILE MOTION The simplest type of motion in a gravitational field near the surface of the Earth is called projectile motion.
As an object of mass m moves
near the surface of the Earth, the net force acting on the object is the
gravitational force FG
|
|
Ian Cooper School of Physics University of Sydney If you have any feedback, comments,
suggestions or corrections please email Ian Cooper ian.cooper@sydney.edu.au |