|
RELATIVE MOTION: POSITION
Ian Cooper email
matlabvisualphysics@gmail.com In analysing the motion of an object or collection of objects,
the first step you must take is to define your frame of
reference and identify the System.
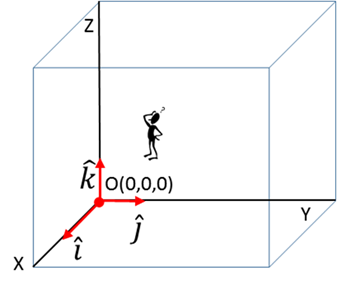
Observer Origin O(0,0, 0) reference
point Cartesian
coordinate axes (X,
Y, Z) Unit
vectors Specify
the units The position of an object (System represented by a point
particle) can be specified by its position vector corresponding to the
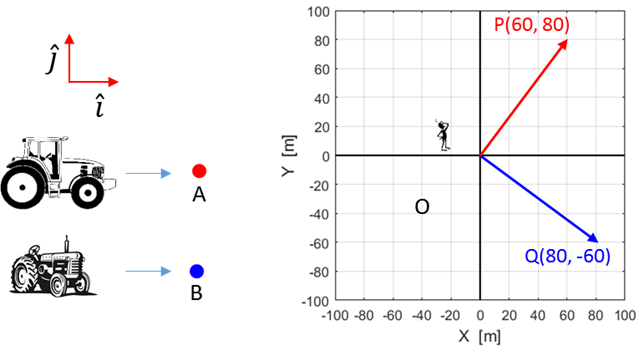
displacement of the system from the Origin O(0, 0). Again, we will consider our two tractors as systems A and B. The
location of the two Systems and their position vectors with respect to the
Origin O(0,) are shown in figure (1). System A is
located at the point P(60, 80) and System B is
located at the point Q(80, -60). The position vectors are System A System B
Fig. 1. The
position vectors (displacements) of the two systems with respect to the
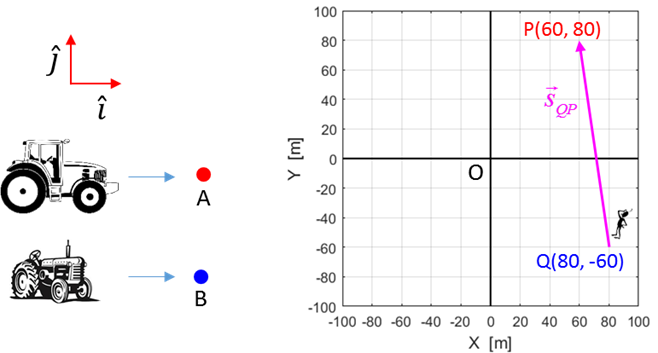
Origin O(0, 0). But what
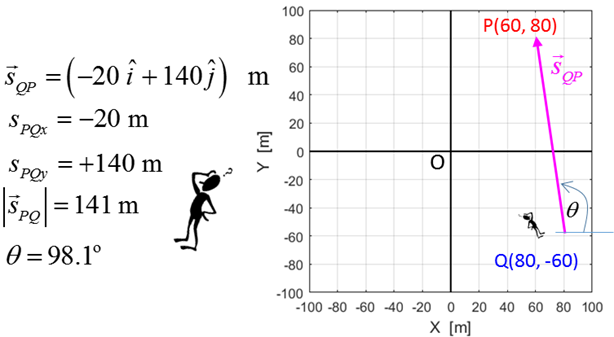
is the location of the tractor A for an observer in tractor B? From the diagram, the point P is 20 m in the negative +X
direction and 140 m in the +Y direction with respect to the point Q.
Also, we can answer this question in terms of the relative position of the
two points using vector quantities. The relative position of point P w.r.t to
the point Q is given by the displacement
Fig. 2. The relative
position of the point P w.r.t. the point Q is given by the vector
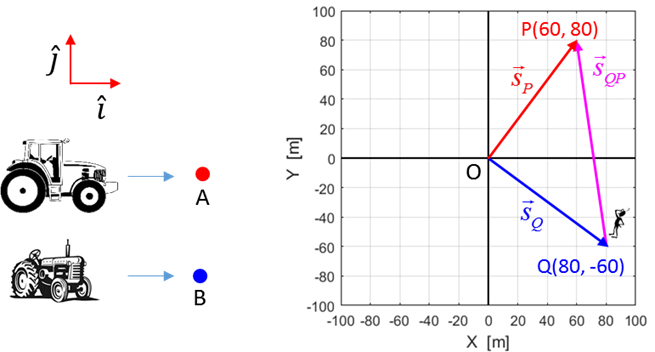
Figure 3 shows the displacement vector
Fig. 3. The
relative position of the point P w.r.t. the point Q is given by the vector From figure (3) using the principle of vector addition it is
obvious that Therefore, the relative position of the point P w.r.t. Q is
given by the vector The relative position in terms of components is System A System B
The magnitude of a vector The direction of the vector is given by
The relative position of point P w.r.t. the point Q is
Fig. 4. Displacement is a relative concept. The relative
position of the point P w.r.t the point Q is given by the displacement
|